What are the types of mechanical compensation in the athermal design of an infrared lens?
1) Mechanical
(electromechanical) active temperature compensation
From the basic theory of optics, we know that when the axial
position of a lens (or lens group) in the optical system is changed, the focal
plane position of the system will change accordingly. Active temperature
compensation uses this principle to reproduce the system. The focus and
adjustment method can be manual or electric. Motorized
IR lens and manual IR lens can be understood as a kind of active mechanical/manual
compensation athermal lens.
To improve the sensitivity of adjustment and maintain the stability
of the optical axis, this temperature compensation method generally requires a
precise mechanical transmission mechanism. At the same time, the required stroke
of the temperature compensation lens should be investigated, and the most
sensitive lens affected by the focusing surface should be selected as the
temperature compensation element.
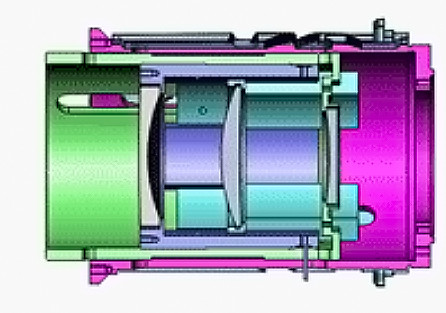
The basic mechanical transmission structure of this compensation
method is basically the same as the focusing mechanism of the optical system.
The method is simple in principle and easy to implement, but it increases the
weight of the optical instrument, and at the same time easily brings about
aiming errors.
2) Mechanical
(electromechanical) passive temperature compensation
The principle of mechanical (electromechanical) passive temperature
compensation is basically the same as that of active temperature compensation,
except that the way of changing the lens group has changed. It uses certain
materials or mechanisms with special functions to realize automatic adjustment.
