What is the difference between infrared images and grayscale images?
Infrared Image Characteristics:
Infrared images are created by “measuring” the heat radiated from objects. Compared to visible light images, they generally have lower resolution, lower contrast, lower signal-to-noise ratio (SNR), a blurry visual effect, and their grayscale distribution is a nonlinear relationship with the reflective characteristics of the target.
Typically, infrared detectors send 16-bit single-channel images, which are converted to 8-bit single-channel images for display. If shown as 24-bit, it implies that R=G=B with each channel at 8-bit.
Why are infrared images sometimes black-and-white and other times color?
Infrared cameras capture grayscale images, similar to a photo in a black and white newspaper. To create color images, grayscale images undergo pseudo color enhancement, where each pixel's grayscale level is transformed into a specific color based on a mapping function, obtaining a color image.
Infrared images are single-channel images, not three-channel images. The color infrared images we see are actually pseudo color images, which are different from the color we see in visible light.
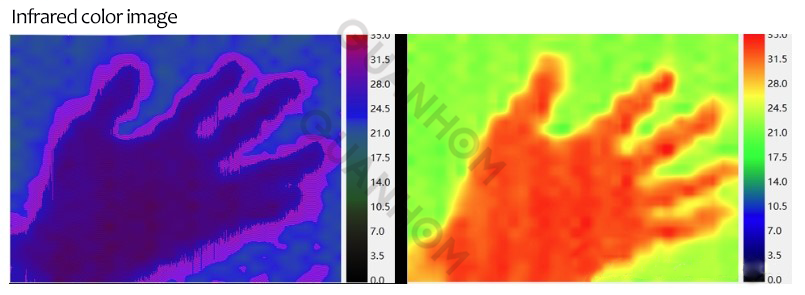

Infrared and Grayscale Images Are Not Based on the Same Classification Standards.
Infrared images are created from the infrared radiation of a target captured by infrared imaging equipment; this image can be either grayscale or color. Similarly, a visible light image can also be either grayscale or color.
Grayscale images are the counterpart of color images; they lack color, with grayscale values ranging from 0 to 255, representing a transition from black to white.
Concept Explanation:
Infrared Image: the intensity of infrared light from an object.
Grayscale Image: the intensity of visible light from an object.
Color Image: Each pixel is composed of R, G, and B components.
Infrared and grayscale images share the same data format as single-channel images, while color images are three-channel images.
