How to Choose|Cooled or Uncooled Thermal Imaging Camera
time2022/05/13

- Over the years, R&D experts have been keen to use thermal imaging cameras in a wide range of applications. However, not all thermal imaging cameras have the same quality features. Today, let's take a look at how to choose between cooled and uncooled thermal imaging cameras!
Over the years, scientists, researchers, and R&D experts have been keen to apply thermal imaging cameras in a wide range of fields, including industrial R&D, academic research, non-destructive testing (NDT) and materials testing, as well as defense and aerospace.
However, not all thermal imaging cameras have the same quality features or can be applied to some specialized fields. For example, accurate measurement requires advanced thermal imaging cameras with high-speed stop-motion animation capabilities. This paper is going to introduce the ways of choosing between cooled and uncooled thermal imaging cameras.
State-of-the-art cooled thermal imaging cameras feature imaging detectors with integrated cryogenic refrigerators. They are devices that reduce the temperature of the detector to a cooling temperature. To reduce thermal noise below the level of the scene imaging signal, a reduction in detector temperature is necessary.
Cooled thermal imaging cameras are the most sensitive thermal imaging cameras, detecting the smallest temperature differences between objects. They operate in the mid-wave infrared (MWIR) and long-wave infrared (LWIR) bands of the spectrum, where thermal sensitivity is higher from a physical point of view. Thermal sensitivity refers to the signal change relative to the target temperature change. The higher the thermal sensitivity, the easier it is to detect those scenes where the target temperature does not differ much from the background.

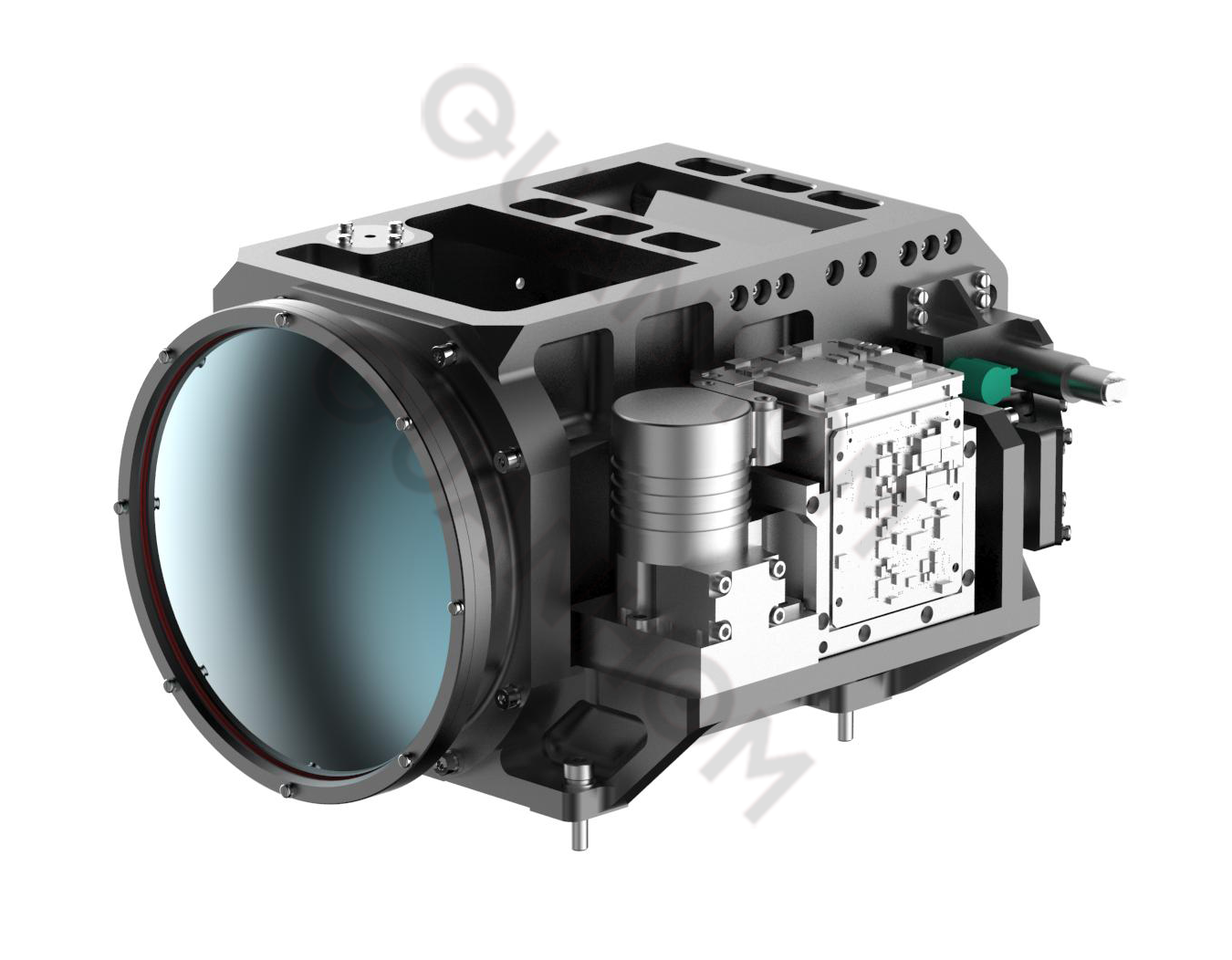
GMZ45055UA: The lens comes with Dewar refrigeration equipment and movement, which can better solve the influence of ambient temperature changes when the equipment is running.
An uncooled thermal imaging camera is an infrared thermal imaging camera in which the imaging detector does not require cryogenic cooling. Common detector designs are based on pyroelectric detectors, which are small vanadium oxide resistors with a large temperature measurement coefficient, large surface area, low heat capacity, and good thermal insulation. Changes in the temperature of the scene will cause the temperature of the infrared detector to change, which will be converted into electrical signals and processed to produce images.
Uncooled detectors are used in the long-wave infrared (LWIR) band, where targets with similar ground temperatures emit the most infrared heat. Compared to refrigerated detectors, uncooled detectors require fewer manufacturing steps, higher yields, and lower cost of vacuum packaging and uncooled thermal imaging cameras do not require extremely expensive cryogenic refrigerator equipment. Uncooled thermal imaging cameras have fewer moving parts and tend to have a longer lifespan than cooled thermal imaging cameras under similar operating conditions.
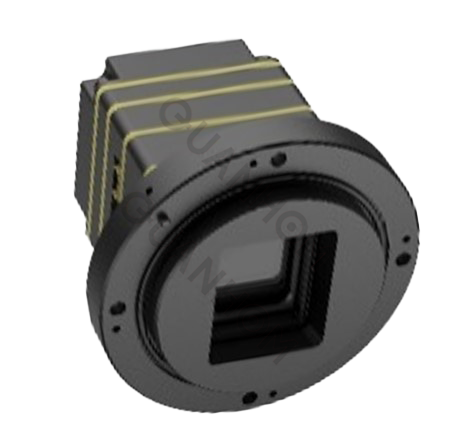

ITH1212IP: ITH1212IP Infrared thermal imaging core is small in size, low in power consumption, and strong in performance
The advantages exhibited by uncooled thermal imaging cameras present a dilemma: when to use cooled thermal imaging cameras for R&D/scientific applications? The answer is: that it depends on the application requirements.
Example comparison:
If you want to spot small temperature differences and need image quality, shoot fast moving or hot objects; if you need to see thermal changes clearly, or measure the temperature of very small objects; if you want to see how objects in very well-defined parts of the electromagnetic spectrum; or if you want to synchronize the thermal imaging camera with other temperature measurement equipment, a cooled thermal imaging camera is the right instrument for you.
1. Speed
Cooled thermal imaging cameras can image faster than uncooled thermal imaging cameras. High-speed thermal imaging has exposure times down to microseconds, stops the apparent motion of dynamic scenes, and captures frame rates of more than 62,000 frames per second. Applications include thermal and dynamic analysis of jet engine turbine blades, automotive tire or airbag inspection, supersonic projectiles, and explosions.
Cooled thermal imaging cameras are extremely responsive and take full advantage of the global shutter. This means they can read out all the pixels simultaneously, rather than line by line like uncooled cameras, allowing cooled cameras to capture sharp images and measure the temperature of moving objects.
2. Spatial resolution
The thermal images below compare the close-up magnification achievable with cooled and uncooled thermal imaging systems. The infrared image on the left was taken with a combined setup with a 4x near-focus lens and a cooled thermal imaging camera with a pixel pitch of 13μm, with a spot size of 3.5μm. The infrared image on the right was taken with a combined setup with a 1x near-focus lens and an uncooled thermal imager with a pixel pitch of 25μm, with a spot size of 25μm.
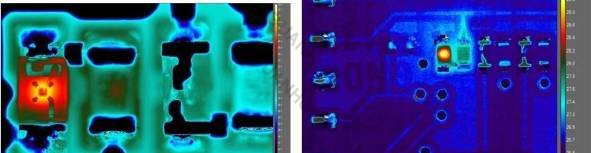
Because of the shorter sensing infrared wavelengths, cooled thermal imaging cameras typically have stronger magnification capabilities than uncooled thermal imaging cameras. Because cooled thermal imaging cameras are more sensitive, lenses with more optics or thicker elements can be used without degrading the signal-to-noise ratio, which improves its magnification performance.
3. Sensitivity
The benefit of improved sensitivity in cooled thermal imaging cameras is often not immediately apparent. To compare the advantages of sensitivity, we performed a quick sensitivity experiment. We created a thermal image of the handprint by pressing our hands against the wall for a few seconds for comparison.
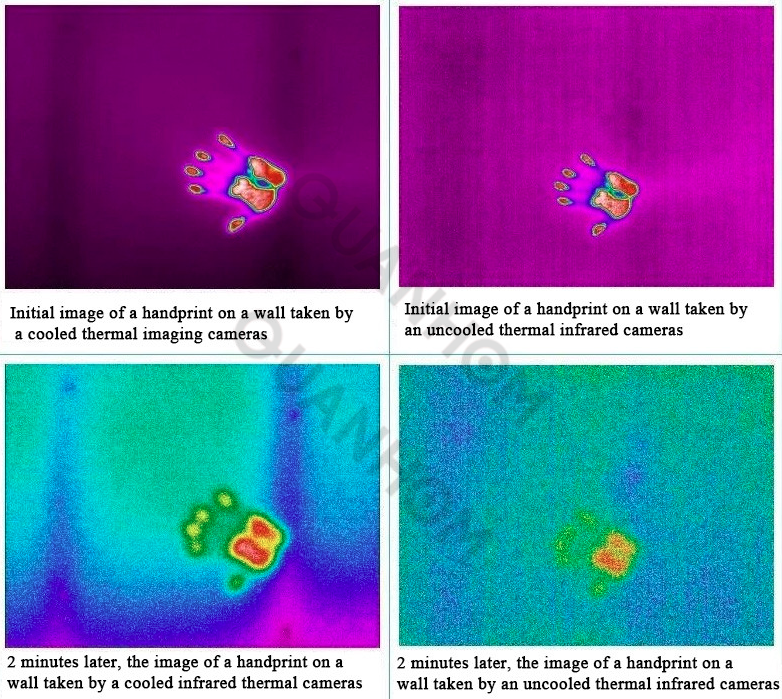
The first two images show the handprint of the moment the hand is removed. The second set of images shows the thermal signature of the handprint after two minutes. The cooled thermal imaging camera can still capture most of the thermal features of the fingerprint, while the uncooled thermal imaging camera can only capture some of its thermal features. Clearly, cooled thermal imaging cameras can detect finer temperature differences than uncooled thermal imaging cameras, and the detection duration is longer. Therefore, cooled thermal imaging cameras show the details of the object being measured more clearly and can help you detect the tiniest thermal anomalies.
4. Spectral Filtering
One of the advantages of cooled thermal imaging cameras is their easy spectral filtering to better detect details and measure temperature, both of which are difficult to achieve with uncooled thermal imaging cameras.
Example: We used a filter that was placed in the filter holder behind the lens or built into the Dewar detector assembly to allow complete imaging of the flame. In the past, end users wished to measure and characterize the combustion of coal particles within a flame. With the "see through flame" spectral IR filter, we have filtered the cooled thermal imaging camera in the spectral band where the flame is penetrating, allowing us to image coal particles. Figure 1 is an image taken without the flame filter; all we see is the flame itself. The second picture is an image taken with a flame filter, and we can clearly see the coal particles burning.
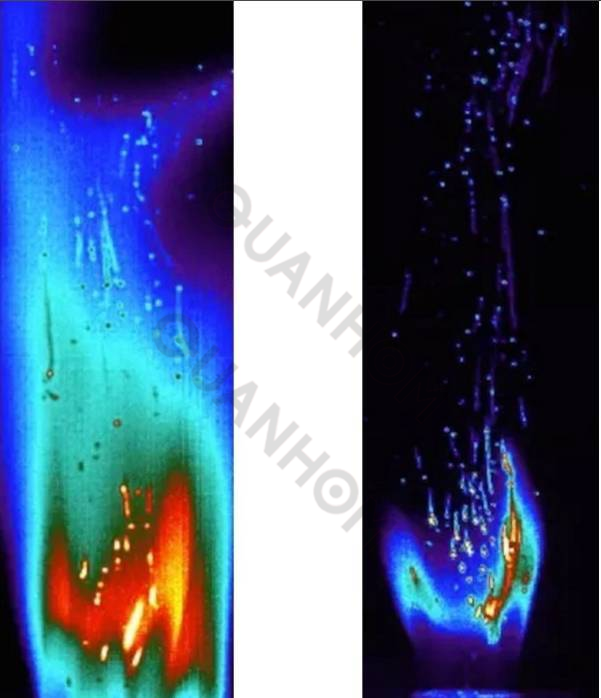
5. Sync
Precise camera synchronization and triggering make the camera ideal for high-speed, thermally sensitive applications. Working in snapshot mode, cooled thermal imaging cameras can simultaneously capture all pixels in thermal activity. This is especially important in monitoring fast-moving objects, and standard uncooled thermal imaging cameras will blur the image.
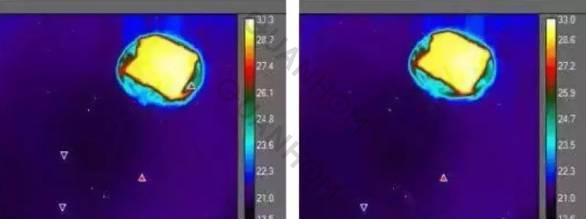
The image above is a good example. We drop a coin, and the sensor triggers the thermal imaging camera to take an image. Tossing the same coin twice, triggering the thermal imaging camera at the same time, we see the object in the same position each time. With an uncooled IR detector thermal imaging camera, you can't catch coins at all because it can't trigger this type of detector. Chances are that the image will be blurry.
To summarize, you can choose between cooled and uncooled thermal imaging cameras according to your application and cost estimation. If you have questions or would like to purchase the related IR products, please contact us.
Quanhom is a professional custom infrared lenses and optical components supplier. Our one-stop solutions to complex challenges in the defense, security, and commercial applications are recognized by customers worldwide. Through innovative design, custom engineering, optical system evaluation, and manufacturing, our multilingual team (English, Spanish, Italian, and Russian) ensure seamless communication from project inception to completion. From consulting to final production, nearly 60 projects are carried out each year. Quanhom's talented team has created many success stories for different applications such as thermal imaging sights for outdoor and defense use, thermal imaging monoculars/binoculars, border, and coastal security, maritime applications, and UAV infrared payloads.
